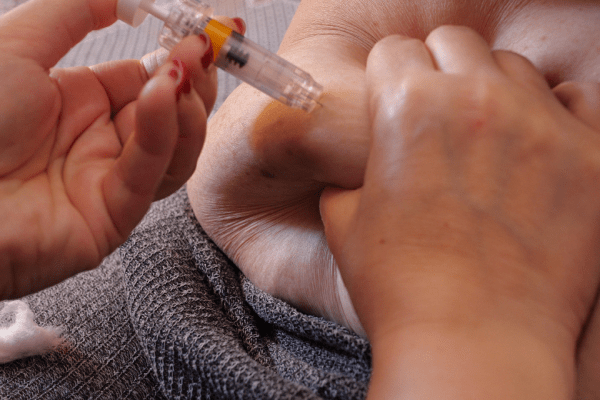
IVF Treatment Process- All Stages
IVF treatment is a treatment for patients who cannot have children. IVF is an assisted reproductive method in which a man’s sperm and a woman’s eggs are combined outdoors in a laboratory dish. One or more fertilized eggs (embryos) can be transferred into the woman’s womb, where they can implant into the uterine lining and develop. Also you will learn more information about Does IVF Get You Pregnant?
What Is IVF?
IVF treatment, which is one of the methods of supplementary treatment for reproducing, begins with the collection of eggs from the mother-to-be and the collection of sperm cells from the father-to-be. The embryo, which emerged after fertilization in the laboratory environment, is placed in the womb of the mother-to-be. At this point, pregnancy continues to be like a naturally acquired pregnancy.

How Is IVF Done?
IVF is a form of assisted reproductive technology (ART). This means that specialized medical techniques are used to help a woman get pregnant. It is most often tried when other cheaper fertility technologies have failed.
There are five basic steps to IVF:
Step 1: Stimulation:
Medications, called fertility medications, are given to a woman to increase egg production. Usually, a woman produces one egg a month. Fertility medications tell ovaries to make more than one egg. During this phase, the woman will regularly undergo transvaginal ultrasound to examine the ovaries and blood tests to check hormone levels.
Step 2: Egg retrieval:
A minor operation, called follicular aspiration, is performed to remove the eggs from the woman’s body. The procedure is usually done in the doctor’s office.The woman will receive medication to avoid pain during the surgery. Using ultrasound images as a guide, the health care provider inserts a thin needle through the vagina into the ovary and sacs (follicles) containing the eggs.
The needle is connected to a suction device, which pulls the eggs and fluid out of each follicle, one at a time. The process is repeated for the other ovary.Cramps can occur after surgery, but they will disappear in one day.
Rarely, a pelvic laparoscopy may be required to remove eggs.If a woman does not produce or is unable to produce eggs, donated eggs may be used.
Step 3: Insemination and Fertilization:
The man’s sperm is placed together with the best quality eggs. Mixing sperm with egg is known as insemination.Eggs and sperm are then stored in an environmentally controlled chamber. The sperm most often enters (fertilizes) an egg a few hours after insemination.If the physician thinks the risk of fertilization is low, the sperm can be injected directly into the egg.This is called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).Many fertility programs commonly make ICSI on some of the eggs, although things look normal.
Step 4: Embryo culture:
When the fertilized egg divides, it becomes an embryo. Laboratory personnel will periodically check the embryo to ensure that it is growing properly. In approximately 5 days, a normal embryo has several cells which actively divide.
Couples at high risk of passing on a genetic (hereditary) disorder to a child may consider preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD).
The procedure is mostly carried out 3 to 5 days after fertilization. Laboratory investigators collect one or more cells from each embryo and analyze the material for specific genetic disorders.According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, PGD can help parents decide which embryos to implant. This decreases the chance of passing a disorder onto a child. The technique is controversial and not offered at all centers.
Step 5: Embryo transfer:
The embryos are placed in the womb 3 to 5 days after the recovery of the eggs and fertilisation.The procedure is carried out at the physician’s office while the woman is awake.The physician inserts a thin tube (catheter) containing the embryos into the woman’s vagina, across the cervix, and into the uterus. If an embryo adheres to (implants) in the wall of the uterus and gets bigger, the pregnancy results. More than one embryo can be placed in the uterus simultaneously, which can lead to twins, triplets or more.The exact number of embryos transferred is a complex problem dependent on many factors, especially the age of the woman.
Unused embryos can be frozen and implanted or donated in the future.

How Likely Is IVF to Succeed?
There are certainly success rates for IVF treatments. However, those rates may vary based on many things that couples have. Therefore, it is not correct to provide a clear success rate. As discussed below, the likelihood that couples will have a live baby following treatment is different for everyone. However, to give an average;
- 32% for women over 35
- 25% for women aged 35-37
- 19% for women aged 38-39
- 11% for women aged 40-42
- 5% for women aged 43-44
- 4% for women over 44
IVF Risks
As for each treatment, there are a few rare risks.
IVF Ectopic Pregnancy: About 2-5% of women who use IVF will have an ectopic pregnancy – when the fertilized egg implants out of the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube. The fertilized egg cannot survive out of the womb and there is no way to keep the pregnancy going.
Birth defects: No matter how the child was conceived, the mother’s age is the major risk factor for birth defects. Further research is required to determine if infants conceived with IVF are at increased risk for certain birth defects.
IVF Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: The use of injectable fertility drugs such as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) to induce ovulation can lead to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, where your ovaries become swollen and painful.
IVF Multiple births: VF involves placing fertilized embryos into the uterus in a laboratory setting. In more than one embryo transfer, the rate of multiple births is high. This results in a higher risk of preterm and miscarriage compared to a single pregnancy.

How Long Does IVF Take to Get Pregnant
Week 1: First visits
During this first meeting, the clinic will obtain from you and your partner many medical histories and attempt to respond to your questions or concerns. During this visit, physicians will examine your diagnosis and the details of your desired treatment plan.
Week 2-4 Preparation Begins
Complete laboratory tests provide a clearer picture of your fertility, so your fertility experts can offer you a personalized IVF protocol.The next step consists in regularizing your menstrual cycle and preparing your ovaries. You can expect to take contraceptive pills for 2 to 4 weeks after screening and diagnosis, depending on how long your cycle is.
Week 5: medication and monitoring
Once you come out of the birth control pill, you will begin a process known as Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation (COH).In the clinic, you will have an ultrasound to assess the uterus and ovaries, and once you get everything clear, you can start.Oral fertility medications like Clomid and/or injectable follicle stimulation hormones (Follistim and Gonal-F) are used to stimulate the follicles in your ovaries to mature more eggs than they typically would in a normal cycle.
The goal is to produce a minimum of 4 eggs with the use of fertility drugs.Ultrasounds and blood tests are used during this period to carefully monitor the development of your follicles and eggs. This is the most time-consuming part of the IVF process, with an average of five to seven office visits.
Week 7: triggering, egg retrieval, and fertilization
After approximately 10-12 days of fertility drugs, monitoring is time to trigger the final maturity of the eggs with hCG and program the acquisition of ultrasound eggs after 36 hours after your follicles have reached a suitable size.
Egg retrieval: This is a one-day operation conducted at the sedated clinic. The risk is minimal, but you will want to take a day off and arrange to have someone pick you up.If you are going through IVF with a partner who will be providing a semen specimen, it will be collected on the same day as your egg retrieval or the sperm could be frozen before.
Egg and sperm are combined in the lab: If everything goes right, fertilization happens and embryos are created. There are several options that can be used at this point to try to improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Within 3-6 days after fertilization, embryos are evaluated for transfer:Daily monitoring helps experts decide which embryos are most likely to survive the transfer, and daily reports from IVF laboratories inform you of their progress.
Embryo or blastocyst transfer: About 3 days after fertilization, the embroyas are ready for transfer, but some patients prefer to wait a few days until they reach the blastoxist stage (usually 5 days after fertilization). The embryo or blastocyst is instilled into the uterus via a thin, flexible plastic tube, which is gently passed through the opening in the cervix leading to the interior of the uterus. You will not be required to sedate for this procedure. It is usually painless, but some women can feel slight cramps. You can see the transfer as it occurs with ultrasonic technology.
After IVF
About 12 days after the embryonic transfer/blastocyst, you will pass your first pregnancy test at the clinic. If it is positive, physicians will program you for pregnancy test 2.
A second test is carried out within one week after the first positive test. If it is positive, physicians schedule you for an ultrasound after 2-3 weeks, and then you can transfer your care to an OB GYN.

Best Country For IVF
There are many countries in the world where IVF treatment is applied, but Thailand is among the most preferred options for high quality and service. Thailand has doctors who specialize in healthcare and speak a foreign language. This makes it a worldwide success with a high degree of satisfaction and success. As clinics, it is the best with advanced equipment, it is intended to provide treatment in the manner.
How Much Does IVF Cost in Thailand
Another reason for Thailand being preferred is reasonable price. You can save about 50 percent of your money as a treatment in Thailand. This means you have an advantage not only in quality but also in price. If you want to receive IVF treatment in Thailand, the price is €4000.
Additionally, this process is more convenient for individuals who want to accommodation package. It includes:
- Round-trip flight ticket for 2 ( air tickets only cover domestic flights )
- Hotel, 7 nights full board
- Taxi transfers and PCR fees included €2000
Below you can see the price list for Thailand with other countries.
| Countries | Price |
| Dubai | The prices of IVF range from €7.000-€9000 |
| The U.S | The average IVF cycle can cost between $13,000 and $19,000 |
| Thailand | The price is €4000. |
We will provide you with the best treatment, and if you want to know more about IVF treatment, our experts will help you every hour of the day.